Being one of the prominent components of HVAC systems, heat pumps, and furnaces both warm the air and make the environment hotter till the set point. But the reason behind the never-ending debate about heat pump Vs. Furnace has not reached the final result yet.
Whether due to structural differences, working abilities, or expensiveness, determining the heat pump vs gas furnace efficiency and choosing the best is challenging.
Therefore, we are here to end this discussion. Let’s move forward and learn about the basic differences between Heat pumps and furnaces so you can decide which is better for you. So, let’s dig in….
What is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is an HVAC system that transfers heat from one place to another. In the winter, it extracts heat from the outdoors and transfers it to your home, keeping you warm. In the summer, it reverses the process, extracting heat from your home and releasing it outdoors, keeping you cool.
Pros of Heat Pumps
- Energy Efficient: Heat pumps are generally more energy efficient than furnaces, especially in moderate climates. This is because they move heat instead of generating it, which requires less energy.
- Dual Function: Heat pumps can both heat and cool your home, eliminating the need for a separate furnace and air conditioner.
- Environmentally Friendly: Heat pumps use electricity to run, which can be produced from renewable sources like solar or wind power. This can help to reduce your carbon footprint.
Cons of Heat Pumps
- Climate Dependence: Heat pumps are less effective in very cold climates. When the outdoor temperature drops below a certain point, the heat pump will have to use its backup heating system, which is usually less efficient.
- Higher Upfront Cost: Heat pumps typically cost more to install than furnaces.
- Maintenance Needs: Heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently.
What is a Furnace?
A furnace is a heating system that burns fuel, such as gas, oil, or propane, to generate heat. The heat is then distributed throughout your home through a network of ducts.
Pros of Furnaces
- Effective in Cold Climates: Furnaces are very effective at heating homes in cold climates. They can provide consistent heat even when the outdoor temperature is low.
- Lower Upfront Cost: Furnaces typically cost less to install than heat pumps.
- Simple Design: Furnaces are relatively simple machines that are easy to maintain.
Cons of Furnaces
- Less Efficient: Furnaces are generally less energy efficient than heat pumps. This is because they burn fuel to generate heat, which wastes some energy.
- Limited Function: Furnaces only provide heat; they cannot cool your home.
- Environmental Impact: Furnaces that burn fossil fuels can contribute to air pollution.
Related : Best Buying Guide for HVAC
Heat Pump vs Furnace: Key differences

Here we have discussed a few of the significant pros and cons of heat pump vs gas furnace in your residential or commercial HVAC system. So, let’s have a quick look at them!
1. Expensiveness:
- Heat Pump: Installation: $4000-$8000, Runs on electricity.
- Furnace: Installation: $2000-$5000, Runs on gas (potentially cheaper depending on location).
2. Efficiency:
- Heat Pump: Serves for both heating and cooling, but efficiency reduces in very cold weather.
- Furnace: Excellent for winter heating, but requires separate cooling system.
3. Maintenance:
- Heat Pump: Lifespan: 15 years, Requires regular maintenance due to more complex operation.
- Furnace: Lifespan: 20 years, Requires less maintenance due to simpler design.
4. Performance:
- Heat Pump: Less effective in extremely cold climates due to reliance on extracting outdoor heat.
- Furnace: Generates heat directly, providing powerful heating regardless of outdoor temperature.
5. Safety:
- Heat Pump: Environmentally friendly, no harmful emissions.
- Furnace: Burns fuel, potentially releasing harmful substances like carbon monoxide.
6. Components:
- Heat Pump: Simpler components: evaporator, compressor, expansion valve.
- Furnace: More complex components: burner, heat exchanger, plenum, blower, ventilation pipes
Gas Furnace vs. Heat Pump
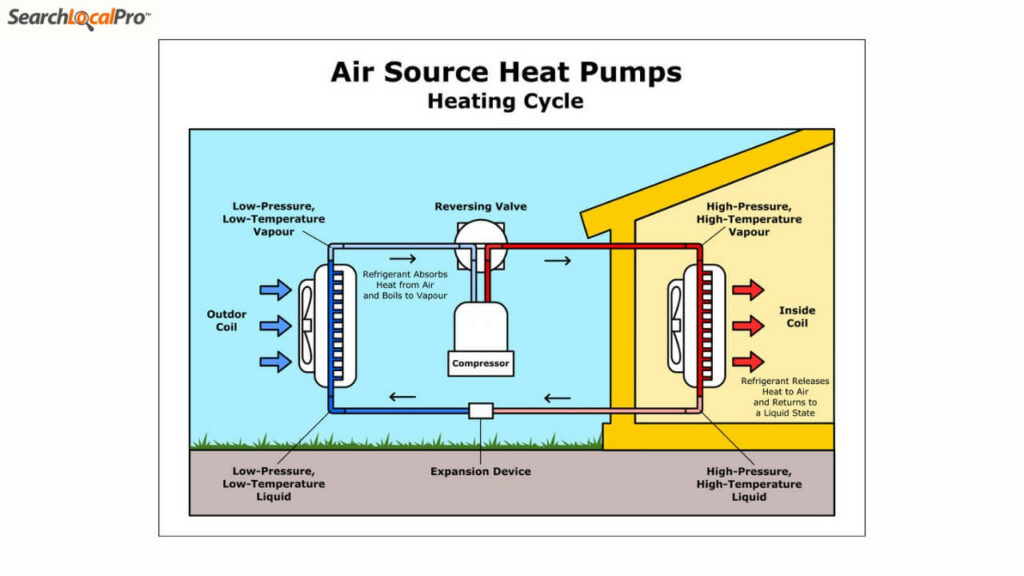
Choosing between a gas furnace and a heat pump depends on several factors, including climate, efficiency, and cost. Here’s a breakdown:
Gas Furnace:
- Pros:
- Lower upfront cost
- More effective in very cold climates
- Generates hot air, providing a toasty feeling
- Cons:
- Less efficient than heat pumps (uses fuel to create heat)
- Requires gas line installation (increases installation cost)
- Not dual-function (heating only)
Heat Pump:
- Pros:
- More energy-efficient (moves existing heat)
- Can function as both heater and air conditioner (dual-function)
- Lower operating costs in moderate climates (uses electricity)
- Cons:
- Higher upfront cost
- Less effective in extremely cold weather (may need backup heat source)
- Doesn’t generate hot air (may feel less comfortable for some)
Oil Furnace Vs Heat Pump
Oil Furnace:
- Pros:
- Effective in cold climates: No problems generating heat even in very low temperatures.
- Fast and powerful heating: Provides a quick and noticeable warm feeling.
- Existing infrastructure: If you already have an oil tank, it might be a lower initial investment (depending on furnace replacement cost).
- Cons:
- Less efficient: Burns oil to create heat, leading to higher operating costs compared to heat pumps, especially with fluctuating oil prices.
- Environmental impact: Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and relies on a non-renewable resource.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance for the furnace and oil tank (potential for leaks and spills).
- Not dual-function: Only provides heating, requiring a separate air conditioning unit for cooling.
Heat Pump:
- Pros:
- Highly efficient: Moves existing heat, resulting in lower operating costs, particularly in moderate climates.
- Environmentally friendly: Uses electricity, potentially with renewable sources like solar panels.
- Dual-function: Heats and cools your home, eliminating the need for a separate AC unit.
- Lower maintenance: Generally requires less maintenance compared to oil furnaces.
- Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: Heat pumps typically cost more to install than oil furnaces.
- Limited performance in extreme cold: Efficiency drops significantly in very cold weather. Some models require backup heat sources (often electric resistance heating) which can be less efficient.
- Climate dependence: Works best in areas with mild winters.
Electric Furnace Vs Heat Pump
Electric Furnace:
- Pros:
- Lower upfront cost: Generally cheaper to install than a heat pump.
- Simple and reliable: Uses familiar electric heating elements for straightforward operation.
- 100% efficient: Converts all electricity used into heat (no energy loss in conversion).
- Readily available: Compatible with most existing electrical wiring.
- Cons:
- Less efficient over time: Electricity rates can be higher than the cost of moving heat with a heat pump, especially in colder climates.
- High operating costs: Can be expensive to run, particularly during extended heating periods.
- Not dual-function: Provides only heating, requiring a separate air conditioning unit for cooling.
- Limited comfort: Electric furnaces generate dry heat, which some people find less comfortable.
Heat Pump:
- Pros:
- Highly efficient: Moves existing heat, resulting in lower operating costs compared to electric furnaces, especially in moderate climates.
- Dual-function: Heats and cools your home, eliminating the need for a separate AC unit.
- More comfortable heat: Heat pumps provide a gentler, more even distribution of warmth compared to electric furnaces.
- Environmentally friendly: Uses electricity, potentially with renewable sources like solar panels.
- Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: Heat pumps typically cost more to install than electric furnaces.
- Limited performance in extreme cold: Efficiency drops significantly in very cold weather. Some models require backup heat sources (often electric resistance heating) which can be less efficient.
- Climate dependence: Works best in areas with mild winters.
- More maintenance: May require slightly more maintenance than electric furnaces due to the additional components involved in heat transfer.
Propane Furnace Vs Heat Pump
Propane Furnace:
- Pros:
- Reliable heat source: Works effectively in very cold climates, consistently generating warmth even in extreme temperatures.
- Fast and powerful heating: Provides a quick and noticeable warm feeling throughout your home.
- Clean burning fuel: Propane burns cleaner than oil, producing fewer emissions.
- Readily available: Propane delivery is common in many areas.
- Lower upfront cost: Generally cheaper to install than a heat pump.
- Cons:
- Less efficient: Burns propane to create heat, leading to potentially higher operating costs compared to heat pumps, especially with fluctuating propane prices.
- Environmental impact: Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, although less than oil. Relies on a non-renewable resource.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance for the furnace and potential tank inspections.
- Not dual-function: Only provides heating, requiring a separate air conditioning unit for cooling.
Heat Pump:
- Pros:
- Highly efficient: Moves existing heat, resulting in lower operating costs compared to propane furnaces, particularly in moderate climates.
- Environmentally friendly: Uses electricity, potentially with renewable sources like solar panels.
- Dual-function: Heats and cools your home, eliminating the need for a separate AC unit.
- Lower maintenance: Generally requires less maintenance compared to propane furnaces.
- Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: Heat pumps typically cost more to install than propane furnaces.
- Limited performance in extreme cold: Efficiency drops significantly in very cold weather. Some models require backup heat sources (often electric resistance heating) which can be less efficient.
- Climate dependence: Works best in areas with mild winters.
So, Which is Better: A Furnace or a Heat Pump?

Answering the question of which is a better option, furnace vs heat pump, is tricky and depends on hundreds of factors.
Whether you bring the increasing price of gas and electricity under the spotlight or think about the need for cool air in summer, only you can decide the best option by getting through your needs.
A heat pump is effective if the summer in your location is extreme and you cannot simply afford to live without a cooling system. Plus the electricity charges are affordable for your comfort.
While getting a furnace is profitable if the winters are freezing, oil, gas, or electricity prices are affordable, and you want a robust warming environment indoors.
Plus, the maintenance and repair needs and cost of the furnace are higher than the heat pump due to the complex components and working process.
Therefore, as you know, warming and cooling systems, whether heat pumps or furnaces, regardless of the types and categories, are certainly not a small or short-term investment; it is best to have a thorough look at your budget and rising prices of natural gas, oil, and electricity and understand your summer and winter needs.
And then, decide whether to install a heat pump or furnace in your home.
Heat Pump Vs. Furnace Common FAQs
Do furnace cools the air in summers?
No, a furnace only warms the indoor air environment in winter. According to thermostat set points, it contains a burner that works on the expenditure of electricity, gas, or oil that produces electricity to heat the indoor air and warm the environment.
Can I use heat pumps in both summer and winter?
Yes, unlike the furnace warming the air in winter only, a heat pump can cool the air in summer and warm it in winter according to your environmental needs.
It works on electricity and warms and cools the air by transferring heat between indoor and outdoor environments.
Which is more efficient; heat pumps or furnaces?
In terms of warmth, the furnace maintains a warmer temperature than heat pumps in winter. At the same time, heat pumps are beneficial and workable in summer and winter.
Moreover, the costs, maintenance, life span, and other aspects are separate for determining the efficiency of both HVAC systems.




